Conjugated to pi bonds. The amino acids are linked through amide or peptide bonds.
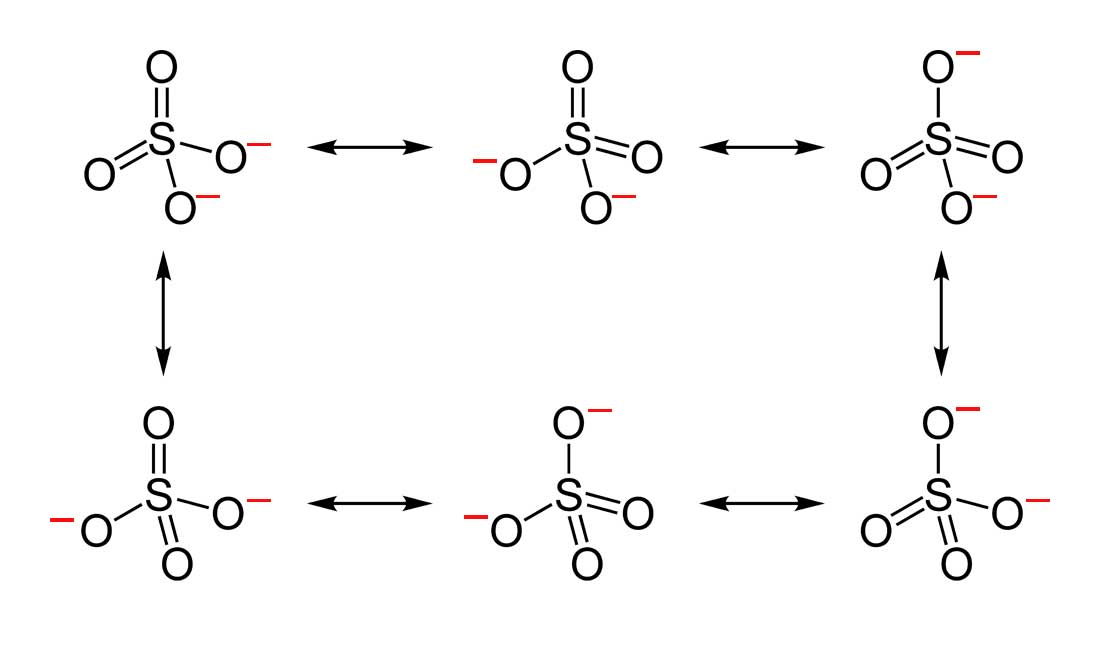
2 6 Drawing Resonance Forms Chemistry Libretexts
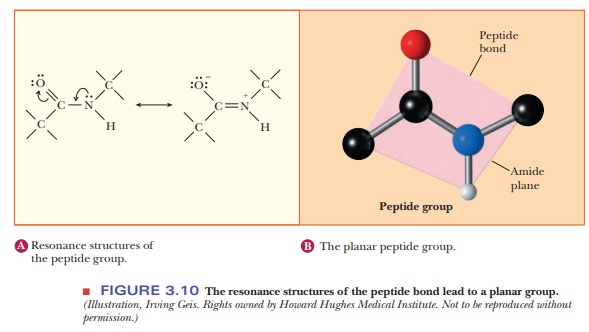
And then to get the residents structure we can move the electrons from this double bond up to the oxygen that we can move this lone pair from nation between the carbon and nitrogen.
. You can never shift the location of electrons in sigma bonds if you show a sigma bond forming or breaking you are showing a chemical reaction taking place see rule 1. 1 has partial double bond character. A peptide bond sometimes mistakenly called amino bond is a covalent bond that is formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the another molecule releasing a molecule of water.
Question Answer MCQ Exam ON. Because the bond between the carbonyl carbon and the nitrogen has a partial double bond character rotation around this bond is restricted. Biosensors And Biochips The resonance structures that can be drawn for the peptide bond indicate that the peptide bond Complaint Here As Incorrect Question Answer Important MCQ on Related Subject Maximum theoretical suction lift for water at 15C by a centrifugal pump is 34 ft.
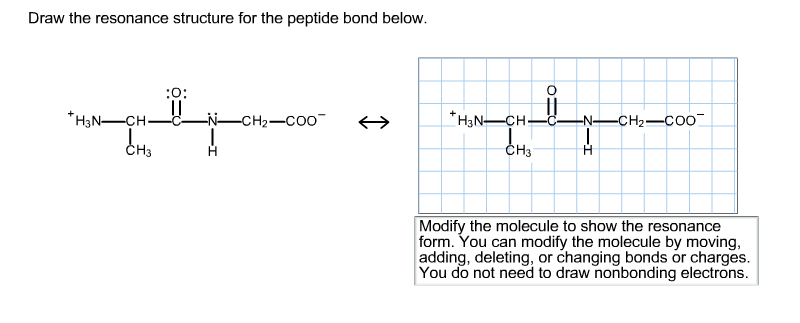
To draw all resonance structures take the lewis structure we drawn by using VESPR rule. You do not need to draw nonbonding electrons. The structure at the right shows a peptide bond between the amino acids valine Val and serine Ser.
2 Resonance contributors involve the imaginary movement of pi-bonded electrons or of lone-pair electrons that are adjacent to ie. 3 is still not completely understood. The resonance structures that can be drawn for the peptide bond indicate that the peptide bond.
24 is asking us to draw the resident structures of the peptide bond so we can start by trying are a peptide bond. Many bridges and buildings have fallen down due to the effects of resonance or to be more precise mechanical resonance 397Å C-C typically 1 In these two forms the pi bond has been rotated 90 Resonance Structures Resonance Structures and Stability This is an important symptom - the vibration in one direction will be. You can never shift the location of electrons in sigma bonds if you show a sigma bond forming or breaking you are showing a chemical reaction taking place see rule 1.
Second because of resonance the peptide bond has partial double-bond character which means that the three non-hydrogen atoms that make up the bond. You can modify the molecule by moving adding deleting or changing bonds or charges. A peptide bond also referred to as an amide bond is formed between the α-nitrogen atom of one amino acid and the carbonyl carbon of a second diagrammed below.
The amino acid sequence from N- to C-terminus determines the primary structure of a peptide or protein. The resonance structures that can be drawn for the peptide bond indicate that the peptide bond. Draw the resonance structure of a peptide bond and explain why there is no rotation around the C-N bond.
The four atoms that are part of the peptide bond are shown as larger spacefilling models. In resonance structures it does not require to show transformation of electrons by arrows. 1 has partial double bond character.
Thus the peptide unit is a planar rigid structure and rotation in the peptide backbone is restricted to the bonds involving the a carbon. The amide structure has two resonance contributors. 2 Resonance contributors involve the imaginary movement of pi-bonded electrons or of lone-pair electrons that are adjacent to ie.
To form a peptide bond a carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another amino acid. Therefore a reasonable resonance structure can be draw with a double bond linking the carbon and nitrogen and which result in a negative charge on the oxygen and a positive charge on the nitrogen. This is a a condensation reaction and usually occurs between amino acids.
4 both and. But to identify each resonance structures it is good to show arrows. 3 is still not completely understood.
4 both and. The Nature of the Chemical Bond and the Structure of Molecules and Crystals3rd ed. The resonance structures that can be drawn for the peptide bond indicate that from CHEM INORGANIC at University of the East Manila.
The amino acids are taken from the crystal structure of hemoglobin αVal 132 and αSer 133. The C-N distance in a peptide bond is typically 132 Å which is intermediate between the values expected for a C-N single bond 149 Å and a CN double bond 127 Å. In following examples arrows are used to show electrons transformation.
As a result a molecule of water is also released. 2 is stronger than an ordinary single bond. Click on the structure below to switch the resonance forms of the peptide bond.
2 is stronger than an ordinary single bond. Draw the resonance structure for the peptide bond below. So-called isopeptide bonds refer to amide bonds between sidechain amines or carbonyl carbons on the side chain rather than α-amine or α-carbonyl.
This is referred to as a condensation reaction. 24 is asking us to draw the resident structures of the peptide bond so we can start by trying are a peptide bond. Conjugated to pi bonds.
Modify the molecule to show the resonance form. A peptide bond is a covalent bond that is formed between two amino acids. And then to get the residents structure we can move the electrons from this double bond up to the oxygen that we can move this lone pair from nation between the carbon and nitrogen.
The resulting bond is a CO-NH bond and is henceforth referred to as a peptide bond. Draw the resonance structure of a peptide bond.
Peptide Bonds Biochemistry Flashcards Draw It To Know It
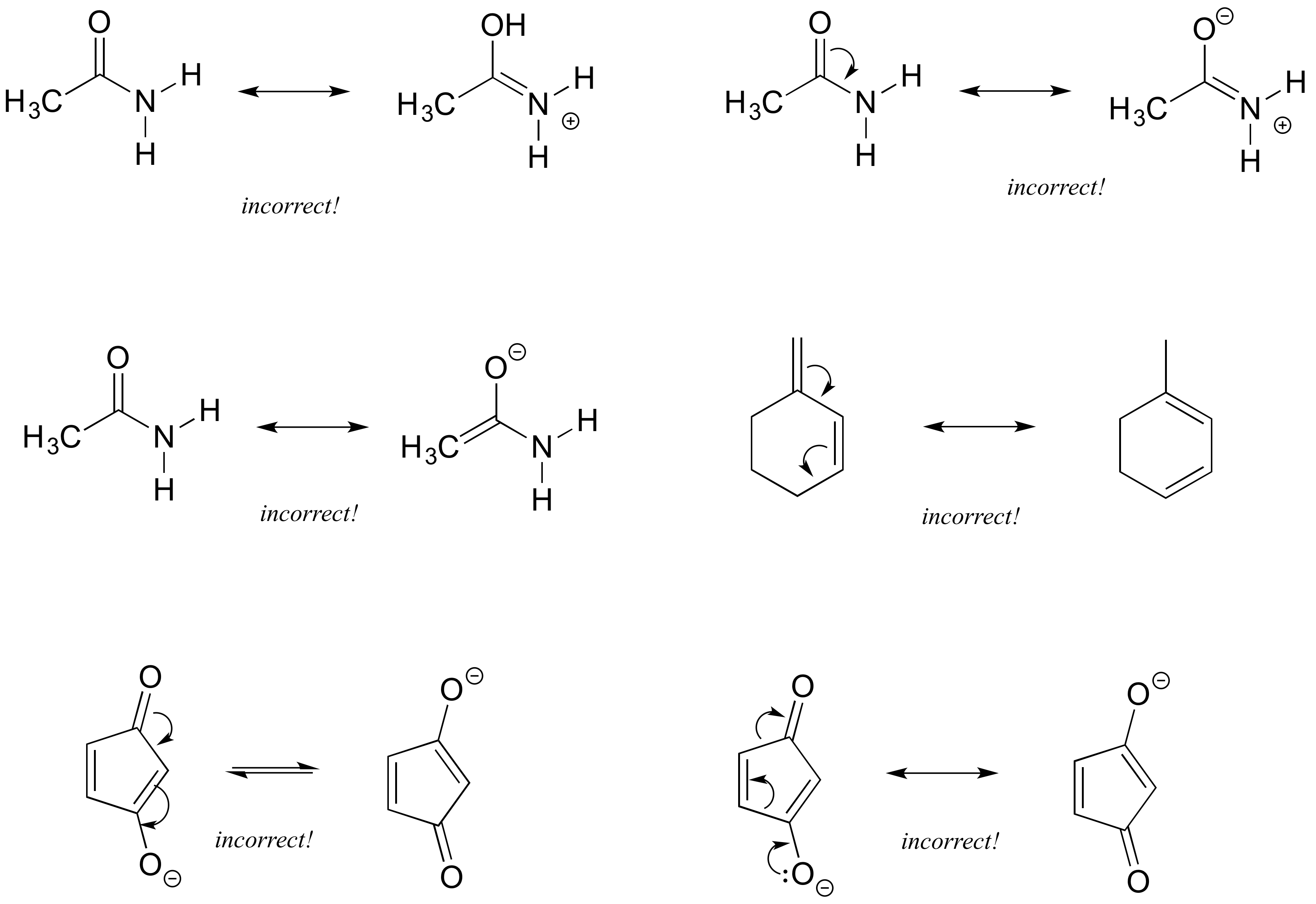
1 4 Resonance Chemistry Libretexts
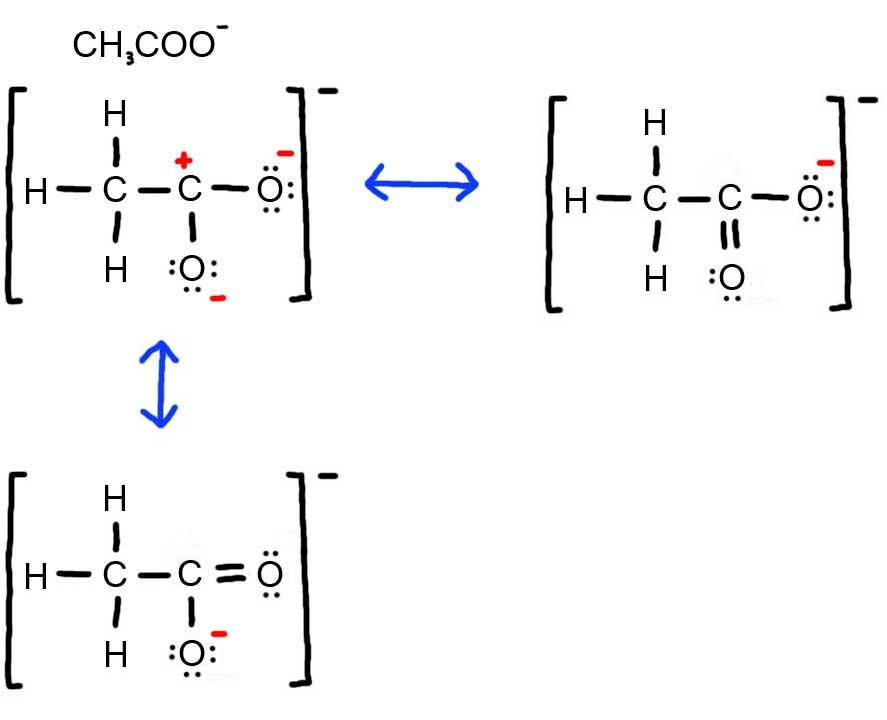
2 6 Drawing Resonance Forms Chemistry Libretexts
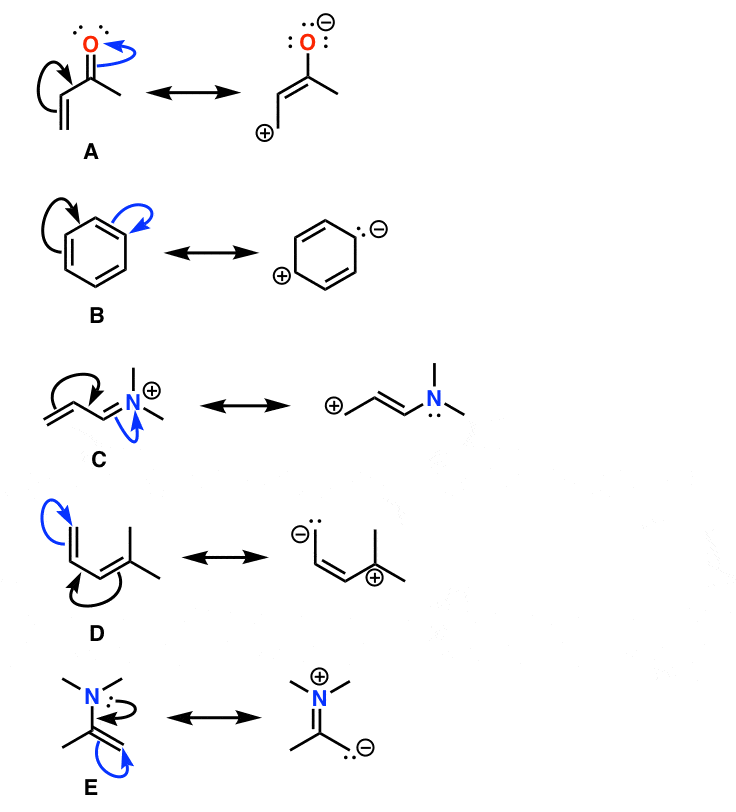
Drawing Resonance Structures 3 Common Mistakes To Avoid
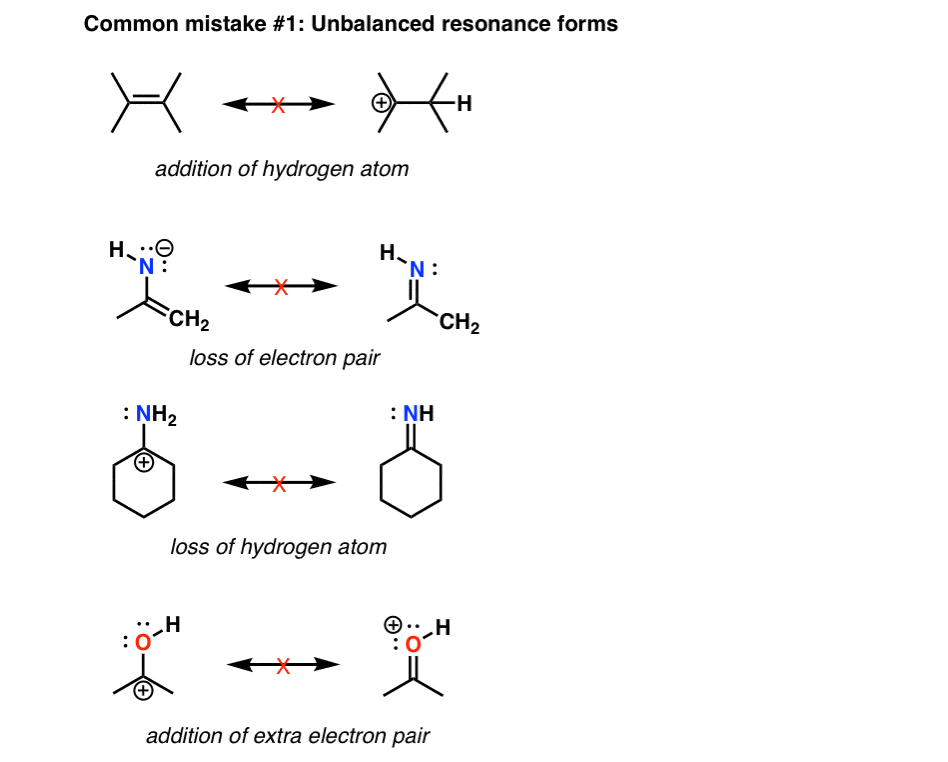
Drawing Resonance Structures 3 Common Mistakes To Avoid

Solved Draw The Resonance Structure For The Peptide Bond Chegg Com

0 comments
Post a Comment